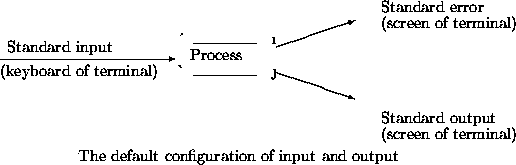
In UNIX systems, there are three special files that are predefined for each process. These special files are

Note that in UNIX everything can be used as a file. A directory, memory, network I/O and even the keyboard are defined as special types of file. Do not get confused with types of a file. When you see file, it means a regular file. Other special files have their own names.
Nearly every program in UNIX sends its output to the standard output, and errors to standard error. Most commands accept file names as arguments and use them as their input, but if no file name is specified, then standard input is used for input. In the example below, cat command will use its predefined standard input, since no file is specified.
<mendelson:~>cat trial and error trial and error is it okay???? is it okay???? why is it repeating them two times? why is it repeating them two times? ^D
As you can see, the command gets each line from the standard input(keyboard) and displays it on standard output (screen). When you press enter, the contents of that line is sent to the command, and it displays them on screen. To tell the command that the standard input is ended (you don't want to enter anything more from keyboard), you should press ^D (Ctrl-d) keys together in a new line. Press the d key for only one instant, don't hold it down. When the command gets this character (^D end of file), it finishes the execution.