 |
A directory may contain several files and directories. A directory can be thought as a book shelf. Directory (shelf) is used to group files (books) and other directories (smaller shelfs) in it. A file (book) may contain only data in it. You can not put another file or directory inside a file.
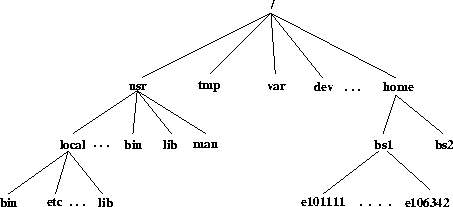
The special character '/' represents the root directory in every UNIX system. This root directory holds every other directory and file in it. The directories inside a directory are called subdirectories. The directory structure grows like a tree which is upside down.
Root directory is at the highest level and each subdirectory is one level below its parent.
When you login, the system lets you start in a predefined directory called home directory. This home directory can not be changed by users. The '~' character represents the home directory.
The links from one directory to some other is called the path of that directory. In the figure above, the path of e101111 directory is "/home/bs1/e101111" (each directory should be separated by '/' character). Path can be represented in three ways. You can start from the root directory (absolute path), from the current directory (relative path) or from the home directory (relative path to home). Users should choose the most suitable one for the current situation. For example if current directory is /home/bs1, a user may write the path to e101111 by "cd /home/bs1/e101111" or "cd e101111" or simply "cd ". The relative path is useful for going to a sub directory of the current directory while absolute path is useful when you know the exact path of the directory, which is not below current directory.
Each directory name can be up to 256 characters provided that it does not include '/' character. It is useful to give meaningful names to directories. The standard directories in each UNIX system are the same. 'bin' directory contains the executable programs of the system. 'var' contains system related directories. 'etc' contains system related configuration files. 'lib' contains library files.
File names have the same properties with directory names. Although the uses are different, directory is also a special type of file in UNIX. Unlike directories, files may not contain subfiles or subdirectories. A path to a file is the same of a path to a directory. Although extensions with a dot means nothing to the system, some applications use them. Frequently used extensions in a UNIX system are
.txt text file .c C source file .cc C++ source file .h header file .z .gz compressed file .gif .jpg image files
The amount of data in a file is called its size. Usually size is expressed in terms of bytes. Directories also have size, but their size depends on the number of files and subdirectories inside them.