


Next: Moderator Specifications
Up: The Language
Previous: The Language
The DARWIN language provides support for domain specification of the
simple types data members of a genetic construct.
By specifying a domain, the compiler is informed about the legal
values for the given data member and it will
generate necessary code in the genetics operators which will guarantee
that no domain violations are resulting. This feature is extremely
useful because the compiler generated initializer, crossover and
mutation function will not be generating illegal solutions, thus
resulting in more intelligent and robust implementations.
The syntax for specifying domains is as follows:
| domain |
::= |
"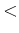 " "[" elements "]" " "[" elements "]" |
| |
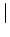 |
"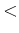 " "{" elements "}" " "{" elements "}" |
| |
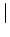 |
/* no domain */ |
Currently, the DARWIN language supports just the range and set
domains. The range domain specifies the upper and lower boundaries
of acceptable values and the set domain lists the possible values
for a construct member.
For example, is a construct member x is of type char and can
only take values in the range [0..100], then it can be declared as
follows:
char x < [0..100];



Next: Moderator Specifications
Up: The Language
Previous: The Language
Gokturk Ucoluk
2003-09-15
" "[" elements "]"
" "{" elements "}"